-
On this page
The OAIC publishes quarterly statistical information about notifications received under the Notifiable Data Breaches scheme, to assist entities and the public to understand the operation of the scheme.
Number of breaches reported under the Notifiable Data Breaches scheme
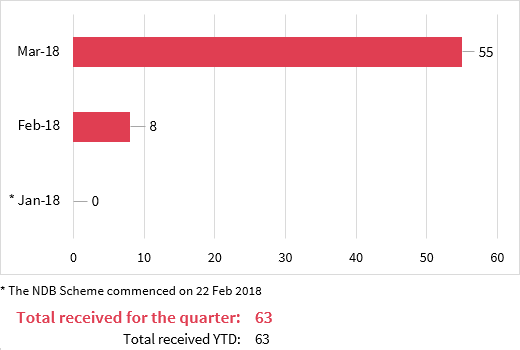
As the NDB scheme commenced on 22 February 2018, data is only available for part of the quarter.
Top 5 industry sectors that reported breaches
in the quarter
| Top 5 industry sectors | NDBs received |
|---|---|
| Health service providers | 15 |
| Legal, Accounting & Management services | 10 |
| Finance (incl. superannuation) | 8 |
| Education | 6 |
| Charities | 4 |
The NDB scheme applies to entities with existing obligations to secure information under the Privacy Act 1988. During the first quarter of 2018, the largest proportion of eligible data breaches reported to the OAIC was from health service providers, at 24 per cent. A health service provider includes any organisation that provides a health service and holds health information.
The second largest proportion was from the legal, accounting and management services sector, at 16 per cent. This was followed by the finance sector (13 per cent), private education sector (10 per cent), and charities (6 per cent).
Kinds of personal information involved in breaches reported in the quarter
| Kinds of personal information | % of NDBs received |
|---|---|
| Contact information | 78% |
| Financial details | 30% |
| Health information | 33% |
| Identity information | 24% |
| Other sensitive information | 2% |
| TFN | 14% |
An eligible data breach may involve one or more kinds of personal information. The majority of data breaches reported to the OAIC involved ‘contact information’, such as an individual’s name, email address, home address or phone number. This is distinct from ‘identity information’, which refers to information that is used to confirm an individual’s identity, such as driver licence numbers and passport numbers.
Entities also reported data breaches that involved individuals’ tax file numbers, financial details, such as bank account or credit card numbers, as well as health information. ‘Other sensitive information’ refers to categories of sensitive information, other than health information, as defined in section 6 of the Privacy Act.
Source of the breaches reported in the quarter
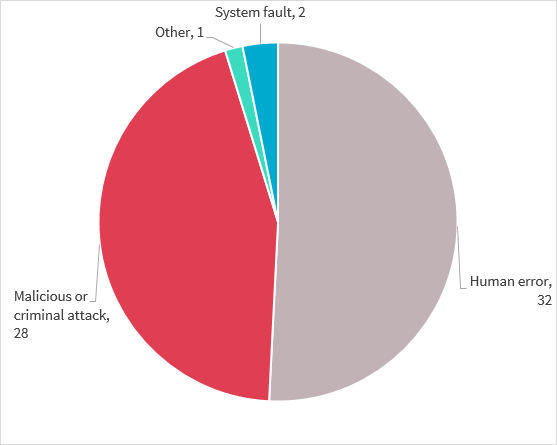
Human error was the cause of the largest number of eligible data breaches reported to the OAIC. Human error may include inadvertent disclosures, such as by sending a document containing personal information to the incorrect recipient.
This was closely followed by malicious or criminal attacks as the source of the data breach. Malicious or criminal attacks usually involve the theft of personal information, or cyber security incidents resulting from unauthorised access to an entity’s systems.
Number of people affected in breaches reported in the quarter
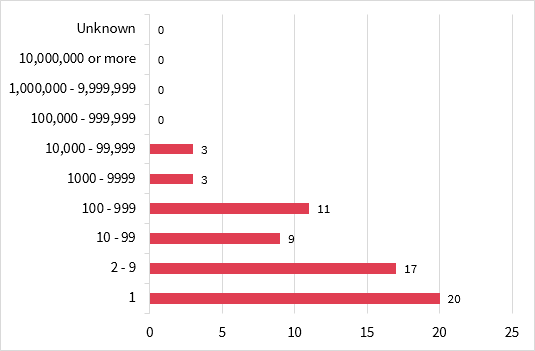
73 per cent of eligible data breaches reported involved the personal information of under 100 individuals, with just over half of the notifications involving the personal information of between 1 and 9 individuals. 27 per cent of notifications under the NDB scheme involved more than 100 individuals.

